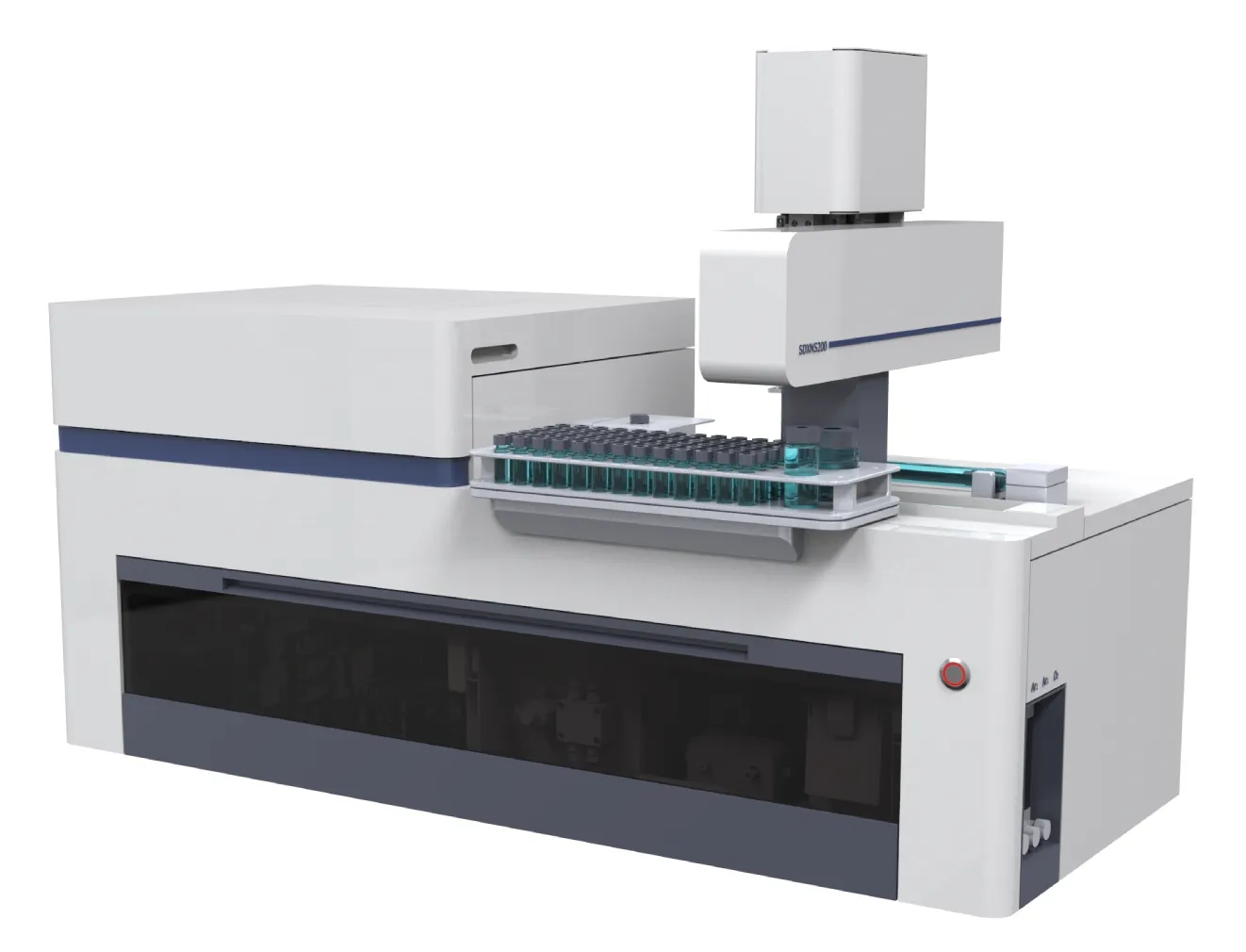
Working Principle
The samples are combusted with oxygen and water vapor in the combustion furnace unit, and the resulting gaseous compounds are absorbed by the absorption solution. The analytes dissolved in the absorption solution are then transferred to the ion chromatography system for determining the concentrations of halogens (fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide) and sulfur.
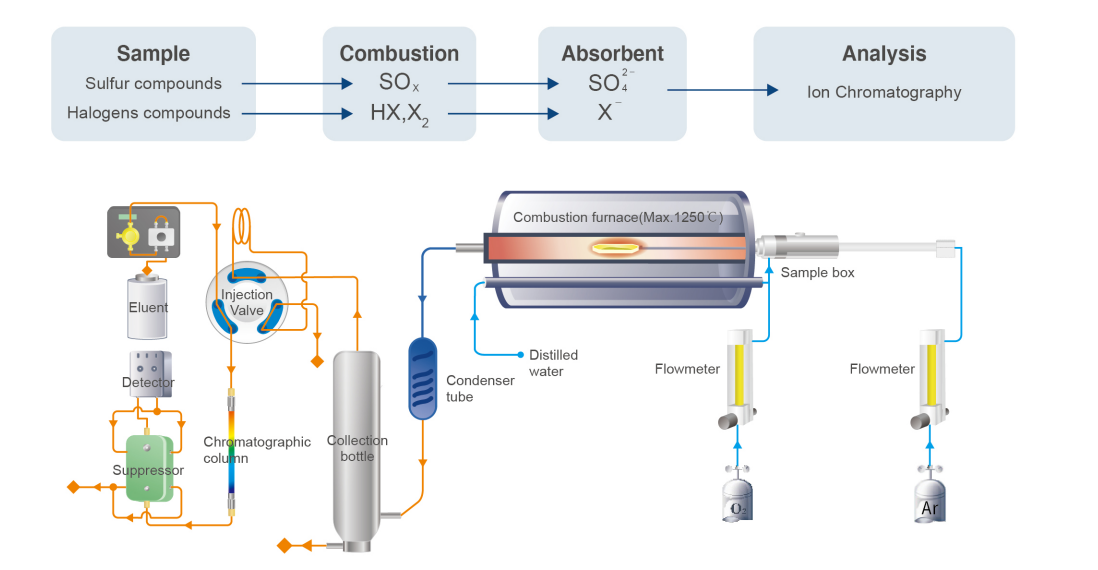
Specification:
Element measured: | F, Cl, Br, I, S |
Sample: | Solid, Liquid, Gas |
Sample mass: | 0-100mg (solid) or 0-100µL (liquid) |
Autosampler: | 49 (solid) or 78 (liquid) |
Furnace temperature: | Max.1250℃ |
Measuring range: | ≥0.2ppm |
Analysis time: | <15min |
Temperature precision: | ±5℃ |
Constant temperature zone: | 14cm |
Gas: | oxygen, argon |
Standard | ASTM D2847 ,ASTM D7359 ,IEC 60754-3,IEC 62321-3-2,GB/T 39560.302,GB/T 42276,GB/T 41067 ,GB/T 43352 ,GB/T 18006.3 ,GB/T 41008 ,GB/T 42908,GB/T 41533,GB/T 39951,GB/T 34845,GB/T 22904,GB/T 40111 |
Highlights
1.High automation
①System preparation: With one-key activation, the combustion furnace automatically heats up, and the IC module starts automatically.
②Sample introduction: Place the sample in the autosampler, input the required sample information and analytical method. The system will then automatically perform combustion pyrolysis according to the preset program.
③Analysis: The sample solution is automatically made up to volume and injected into the IC module, with the flow path automatically cleaned. Automatic dilution is optional for high-concentration samples.
④Results are automatically calculated, and blank values are automatically deducted.
⑤Fault Handling: The system automatically prompts for faults and provides troubleshooting methods. Individual components can be tested separately via the manual detection interface.
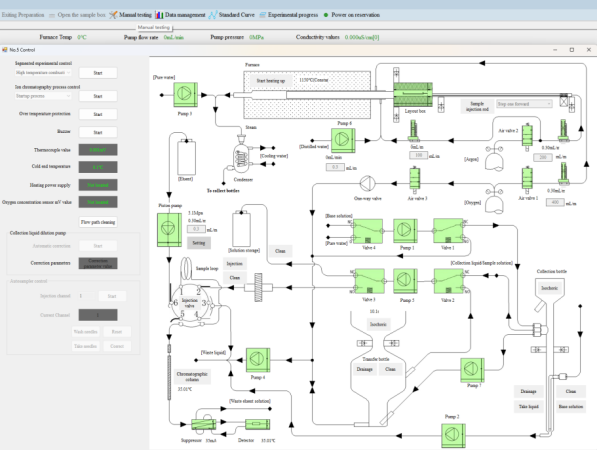
2.Wide sample compatibility
①Supports solid, liquid, and gas samples.
②Pyrolysis atmospheres can be selected according to specific needs, including oxygen, air, argon, nitrogen, and water vapor.
③Fully configurable combustion-pyrolysis parameters, including sample introduction time, sample introduction distance, retention time, and water vapor flow rate.
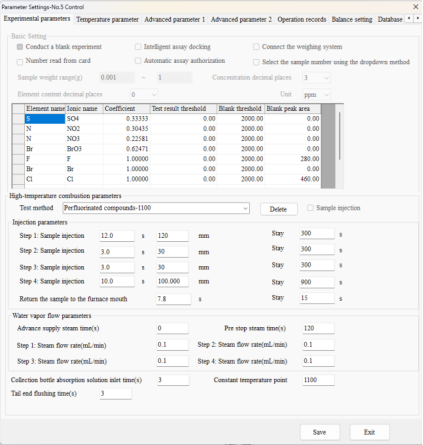
3.High efficiency
①Simultaneous sulfur and halogens determination, with automatic data calculation and direct LIMS upload minimizes manual errors.
②Calibration curves for various concentration ranges can be prepared to reduce repetitive testing.
4.Wide measuring range, low quantitation limit
Based on a 50mg sample, the limit of quantitation (LOQ) up to 0.2 mg/kg(200ppb). Theoretically, the maximum concentration can be up to 100%.
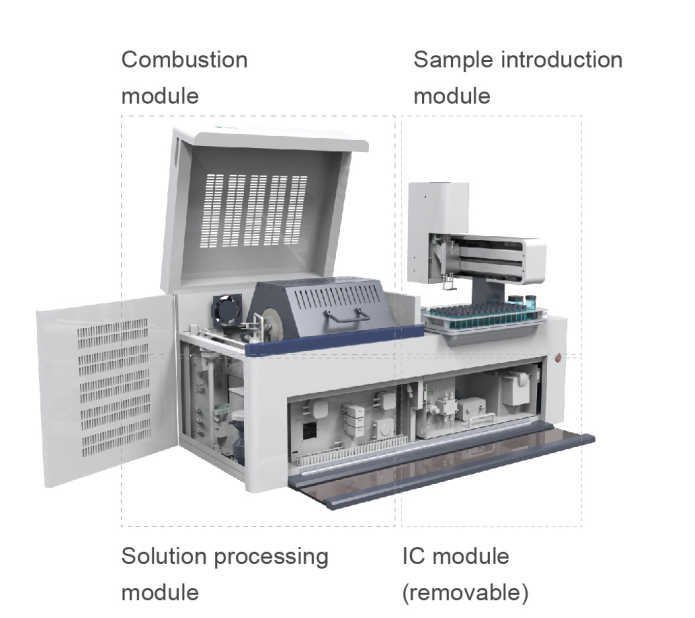
5.Easy maintenance and disassembly
①Modular design enables easy replacement of combustion tubes, sampling rods, and chromatographic columns.
②Sundy CIC system can be used independently as a combustion-pyrolysis furnace or an ion chromatography.
System blank test
1.Test procedures
Without adding any sample, follow the routine sample testing procedure and conduct multiple consecutive tests until the system blank no longer decreases. This value is defined as the minimum system blank of this instrument.
2.Combustion conditions

Combustion process
Step | Sample Introduction Time (s) | Distance (mm) | Retention Time (s) |
Step 1 | 17 | 200 | 100 |
Step 1 | 30 | 30 | 100 |
Step 3 | 30 | 40 | 100 |
Step 4 | 30 | 40 | 450 |
3.IC conditions

4.Test results
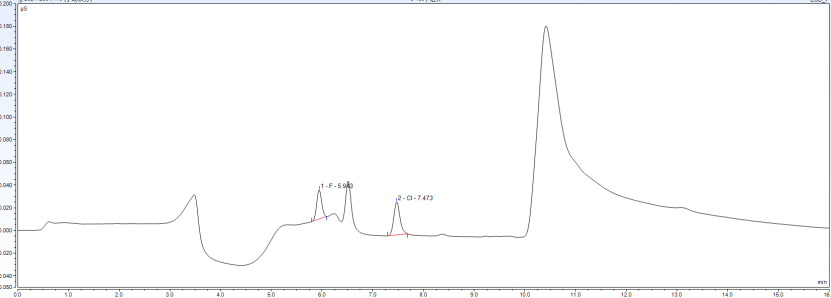
S/N. | F | Cl | Br | SO4 | ||||
Conc. (mg/L) | Peak area | Conc. (mg/L) | Peak area | Conc. (mg/L) | Peak area | Conc. (mg/L) | Peak area | |
1 | 0.0004 | 0.0052 | 0.0004 | 0.0055 |
|
|
|
|
2 | 0.0004 | 0.0049 | 0.0004 | 0.0054 |
|
|
|
|
3 | 0.0004 | 0.0053 | 0.0004 | 0.0055 |
|
|
|
|
4 | 0.0004 | 0.0052 | 0.0004 | 0.0052 |
|
|
|
|
5 | 0.0004 | 0.0054 | 0.0004 | 0.0054 |
|
|
|
|
6 | 0.0004 | 0.0052 | 0.0004 | 0.0052 |
|
|
|
|
Aver. | 0.0004 | 0.0052 | 0.0004 | 0.0054 |
|
|
|
|
RSD(%) | 0 | 3.22 | 0 | 2.55 |
|
|
|
|
Conc. based on 50mg sample (ug/kg) | 80 |
| 80 |
|
|
|
|
|
Standard solution recovery test
1.Test procedures
Transfer an appropriate volume of the standard solution onto ignited quartz wool in the crucible. Start the test according to the set testing procedures. After the test is completed, calculate the measured concentration by deducting the blank value, and then divide it by the theoretical concentration to obtain the recovery rate of the standard solution.
2.Combustion conditions

Combustion process
Step | Sample Introduction Time (s) | Distance (mm) | Retention Time (s) |
Step 1 | 17 | 200 | 100 |
Step 1 | 30 | 30 | 100 |
Step 3 | 30 | 40 | 100 |
Step 4 | 30 | 40 | 450 |
3.IC conditions
4.Test results
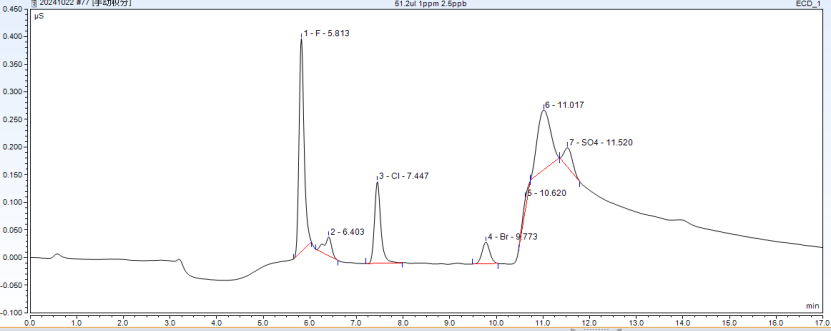
S/N. | Theoretical Conc. (ug/L) | Measured Conc. (ug/L) | Recovery (%) | ||||||
F | Cl | Br | SO4 | F | Cl | Br | SO4 | ||
1 | 2.5 | 2.33 | 2.61 | 2.49 | 2.46 | 93.20 | 104.40 | 99.60 | 98.40 |
2 | 2.27 | 2.43 | 2.46 | 2.39 | 90.80 | 97.20 | 98.40 | 95.60 | |
3 | 2.43 | 2.56 | 2.51 | 2.33 | 97.20 | 102.40 | 100.40 | 93.20 | |
4 | 2.33 | 2.58 | 2.49 | 2.41 | 93.20 | 103.20 | 99.60 | 96.40 | |
5 | 2.21 | 2.42 | 2.56 | 2.45 | 88.40 | 96.80 | 102.40 | 98.00 | |
6 | 2.25 | 2.38 | 2.48 | 2.36 | 90.00 | 95.20 | 99.20 | 94.40 | |
Aver. | 2.30 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.40 | 92.13 | 100.00 | 99.93 | 96.00 | |
RSD(%) | 3.37 | 3.91 | 1.37 | 2.11 | 3.37 | 3.91 | 1.37 | 2.11 | |
S/N. | Theoretical Conc. (ug/L) | Measured Conc. (ug/L) | Recovery (%) | ||||||
F | Cl | Br | SO4 | F | Cl | Br | SO4 | ||
1 | 10 | 10.01 | 9.81 | 9.72 | 9.67 | 100.10 | 98.10 | 97.20 | 96.70 |
2 | 9.87 | 9.48 | 9.81 | 9.81 | 98.70 | 94.80 | 98.10 | 98.10 | |
3 | 9.92 | 9.58 | 9.72 | 9.78 | 99.20 | 95.80 | 97.20 | 97.80 | |
4 | 9.81 | 9.71 | 9.81 | 9.36 | 98.10 | 97.10 | 98.10 | 93.60 | |
5 | 9.78 | 9.61 | 9.58 | 9.69 | 97.80 | 96.10 | 95.80 | 96.90 | |
6 | 9.88 | 9.72 | 9.71 | 9.61 | 98.80 | 97.20 | 97.10 | 96.10 | |
Aver. | 9.88 | 9.65 | 9.73 | 9.65 | 98.78 | 96.50 | 97.25 | 96.53 | |
RSD(%) | 0.83 | 1.22 | 0.87 | 1.67 | 0.83 | 1.22 | 0.87 | 1.67 | |
 0086-731-88112150 sales@sandegroup.com
0086-731-88112150 sales@sandegroup.com 










 0086 731 88112150
0086 731 88112150 0086 731 88134650
0086 731 88134650 sales@sandegroup.com
sales@sandegroup.com